Wednesday, August 30, 2006
Tuesday, April 11, 2006
Seminar report
here is the link
http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~ajitb/seminar/
Thursday, April 06, 2006
Types of queries
- Whole Match Queries: Given a collection of N objects O1,.., On and aquery object Q find data objects that are within distance delta from Q
- Sub-pattern Match: Given a collection of N objects O1,.., On and a query(sub-) object Q and a tolerance delta identify the parts of the data objects that match the query Q.
- K- Nearest Neighbor queries: Given a collection of N objects O1,.., On and a query object Q find the K most similar data objects to Q.
- All pairs queries (or ”spatial joins”): Given a collection of N objects O1 ,.., On find all objects that are within distance delta from each other.
- Visibility - What can I see?
- Ray intersections - What did the player just shoot?
- Collision detection - Did the player just hit a wall?
- Proximity queries - Where is the nearest power-up?
Why are apatial access methods important
Clustering is needed to group those objects which are often requested together. Otherwise, many different disk pages will have to be fetched, resulting in slow response. For spatial selecting the clustering implies storing objects which are close together in reality also close together in the computer memory (instead of scattered over the whole memory).
In traditional database systems sorting (or ordering) the data is the basis for efficient searching. Higher dimensional data can not be sorted in an obvious manner, as it is possible for text strings, numbers, or dates (one-dimensional data). Basically, computer memory is one-dimensional. However, spatial data is 2D, 3D (or even higher) and must be organized somehow in the memory. An intuitive solution to organize the data is using a regular grid just as on a paper map. Each grid cell has a unique name; e.g. ’A3’, ’C6’, or ’D5’. The cells are stored in some order in the memory and can each contain a (fixed) number of object references. In a grid
cell, a reference is stored to an object whenever the object (partially) overlaps the cell. However, this will not be very efficient due to the irregular data distribution of spatial data: many cells will be empty, e.g. in the ocean, while many other cells will be overfull, e.g. in the city center. Therefore, more advanced techniques have been developed.
Representing image through quadtree
To summarize, a square or quadrant in the picture is either :
- entirely one color
- composed of 4 smaller sub-squares
Now consider the following image :
The definition of a picture is a two-dimensional array, where the elements of the array are colored points .
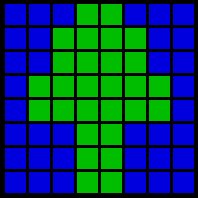

Given Image in pixel form In Quad tree-form
Now when this image is represneted as quad tree it will look like :
 The quad tree of the above example picture. The quadrants are shown
The quad tree of the above example picture. The quadrants are shownin counterclockwise order from the top-right quadrant. The root is the top node.
(The 2nd and 3rd quadrants are not shown.)
the corresponding leaves. The final formula used for the similarity matching(SM) is the following:
weighting of the two metrics.
Monday, March 27, 2006
How is Multimedia Data different
The content of multimedia data is often captured with different “capture” techniques (e.g., image processing) that may be rather unreliable. Multimedia processing techniques need to be able to handle different ways of content capture including automated ways and/or manual methods.
Queries posed by the user in multimedia databases often cannot come back with a textual answer. Rather, the answer to a query may be a complex multimedia presentation that the user can browse at his/her leisure. Our framework shows how queries to multimedia databases may be used to generate multimedia presentations that satisfy users queries-a factor that is unique to our framework.
Multimedia data is large and affects the storage , retrieval and transmission of multimedia data.
- In case of video and audio databases time to retrieve information may be critical ex(Video on demand).
Automatic feature extraction and Indexing: In conventional databases user explicitly submits the attribute values of objects inserted into the database. In contrast, advanced tools such as image processing and pattern recognition tools for images, to extract the various features and content of multimedia objects. As size of data is very large we need special data structures for storing and indexing.
Sunday, March 26, 2006
Types of Multimedia Data
Text : The form in which the text can be stored can vary greatly. In addition to ASCII based files, text is typically stored in processor files, spreadsheets, databases and annotations on more general multimedia objects. With availability and proliferation of GUIs, text fonts the job of storing text is becoming complex allowing special effects(color, shades..).
Images : There is great variance in the quality and size of storage for still images. Digitalized images are sequence of pixels that represents a region in the user's graphical display. The space overhead for still images varies on the basis of resolution, size, complexity, and compression scheme used to store image. The popular image formats are jpg, png, bmp, tiff.
Audio : An increasingly popular datatype being integrated in most of applications is Audio. Its quite space intensive. One minute of sound can take up to 2-3 Mbs of space. Several techniques are used to compress it in suitable format.
Video : One on the most space consuming multimedia data type is digitalized video. The digitalized videos are stored as sequence of frames. Depending upon its resolution and size a single frame can consume upto 1 MB. Also to have realistic video playback, the transmission, compression, and decompression of digitalized require continuous transfer rate.
Graphic Objects: These consists of special data structures used to define 2D & 3D shapes through which we can define multimedia objects. These includes various formats used by image, video editing applications.
Monday, March 13, 2006
Multimedia Indexing
- Provide a measure for the distance between two multimedia objects :
So we need to define a distance function D().Given two objects OA, OB the distance (=dis-similarity) of the two objects is denoted by D(OA, OB). It can be Euclidean Distance . - Similarity Queries :
- Whole query matches : for a query of object O , find the objects within the database which are with in similarity distance delta from O.
- Sub-pattern Match : Given a collection of N objects O1,…, ON and a query (sub-) object Q and a tolerance delta identify the parts of the data objects that match the query Q .
- Or we can find k nearest neigbours of object queried.
- Whole query matches : for a query of object O , find the objects within the database which are with in similarity distance delta from O.
- Algorithm : Sequential scanning and distance calculation with each and every object is too slow for large databases. We can use highly fine-tuned database SAMs (Spatial Access Methods) like R-trees to accelerate the search (by pruning out large portions of the database that are not promising) .
Wednesday, March 08, 2006
Case Studies
InterBase is a relational Database that has builtin support for BLOBs. It has its own interface to relational database that it manages. InterBase stores BLOBs in collection of segments. A segment in InterBase can be thought of as a fixed-length "page" or I/O block. InterBase provides special API calls to retrieve and modify segments. It allows user to open-BLOb , create-BLOB, read segmet (by get-segment) and write a segment to BLOB (put-segment).
Sybase's SQL Server supports TEXT and IMAGE data types. TEXT and IMAGE data-types can be very large up to 2GB. User can defien table as :
CREATE TABLE Page (
Number Integer ,
Content IMAGE ,
Anstract TEXT)
In terms of their internal storage representation TEXT and IMAGE column values contain pointer to firest page of multimedia column. The pages are stored as linked-list. The pages od TEXT and IMAGES colums are stored seperately fro tables of database.
XDP from Plexus is imaging database engine that provide support for BYTES and TEXT data types. A special family can be assigned to each IMAGE and TEXT column in a Table with a different storae extent or family for that tabel recors. Example :
CREATE TABEL Pages
(Number Intege,
PageImage IMAGE IN ImageFamily)
IN CompoundDocumentFamily
XDP supports hierarchial storage system, managing magnet disks, optical disks, optical jukeboxes with online, near-line (stored in the optical jukeboxes but not munted), and offline stored on a shelf) devices.
MultiMedia Datatypes in UniSQL/X Being an object relationa; database management system , UNiSQL supports most of SQL constructs. FOr multimedai data types UniSqL/X supports a class hierarchiay rooted at generalized large object (GLO) class. This class serves as the root od multimedia data types and provides a number of builot-in attributes and methods for instatiating and inheriting clients.For content of GLO objetcs user can create either Large Object (LO) or a File Based Object(FBO) . An interestin gfeature is that recovery is supported for FBOs but consisteny is not supported as external application can aloso access it. LOs are similar to BLOBs in relational databases. FBOs are stored in host file system. Two other subclasses are Audio and Image class. Audio serve as root class of various type of audio classes. Image class is the root of image types, including 2D and 3D images. It supports number of attributes and ethods(also inherited from parent classes) to support storing and manipulating data.

About me
- I'm Ajit Burad
- From Pune, India
- This Blog has moved to new home, Check it here: http://aburad.com/blog/